
Transfer learning is when a machine learns from a set of example tasks. A trained model will predict the outcome in any given situation. Transfer learning is not only helpful for prediction but also for fine-tuning the model. Nowadays, many research institutions have made their trained models available to the public. Deep learning is just one application of transfer-learning. Deep learning can help you identify key features of the problem and determine which representation is best. Deep learning can yield better results than human beings.
Machine learning
Transfer learning from machine learning is a method for transferring machine learning knowledge from one domain to another. This technique is common in the natural language processing area, where AI models can be trained to understand linguistic structure and predict the next word in an sentence based off previous words. The same model can be used for German voice recognition. This same principle can be used to create models that allow for autonomous truck and car driving.
Unsupervised transfer of learning
While supervised transfer learning uses the same labelled data as supervised learning, unsupervised transfer learning removes the need for labelled data. Unsupervised transfer learning uses a class known as autoencoders. Autoencoders learn to perform a specific task (e.g. image reconstruction) but can be fine-tuned so that they can do the target task. This thesis examines the effectiveness of autoencoders in pre-training tasks. It uses state-of-the art autoencoder design findings and applies modifications to maximize their unsupervised transfer learning performance.

Heterogeneous transfer learning
Transfer learning can be approached in many different ways. Each method has its own unique features. Hybrid approaches combine Deep Learning techniques with asymmetric maps to resolve bias issues in cross-domain correspondences. This approach needs both labeled and unlabeled data for correspondence. Both approaches assume the data to be representative of both the source as well as the target domains. This section will outline several common ways of transferring knowledge.
Feature augmentation operations
Combining features can improve machine learning algorithms. One of the most popular methods is SMOTE. It is a combination two augmentation techniques. It generates N2 + n. It can also be stacked with other augmentation methods. Krizhevsky et al. Krizhevsky et al. demonstrate that this method can double the size of a dataset by 2048.
Feature transformation operations
Feature transformation operations use algorithms to align features between a source domain and a target domain. Two steps are typically involved in these operations: obtaining orthonormal bases to the source and target domains, and learning how to shift between them. The first step is to train a classifier with traditional methods on the transformed instances. Feature conversion operations are crucial to transfer learning algorithms. In this article, we will discuss how to apply them. In this article, you will learn how to use feature transform operations in transferlearning.
Co-clustering based classification (CoCC)
A new classification algorithm was developed to address the problem of learning with in-domain knowledge. It uses Co-clustering as a bridge for propagating class structure and knowledge. This algorithm can be used to classify tasks in both unsupervised and supervised environments. However, this algorithm is more complex if there are many word clusters. In this article, we discuss the main features of this algorithm. Before we can understand the potential uses of this algorithm, let's first talk about its advantages and disadvantages.
Transfer Component Analysis
Transfer Component Analysis looks for components that can cross domains. For example, in a brain-computer interface (BCI), the motion intention of an individual can be detected through the EEG signals. It is difficult to continue using BCI because of the nonstationarity and irregularities of EEG signals. Researchers have developed a new technique called Transfer Component Analysis (TCA), which can be used for determining damage.
FAQ
Who is leading the AI market today?
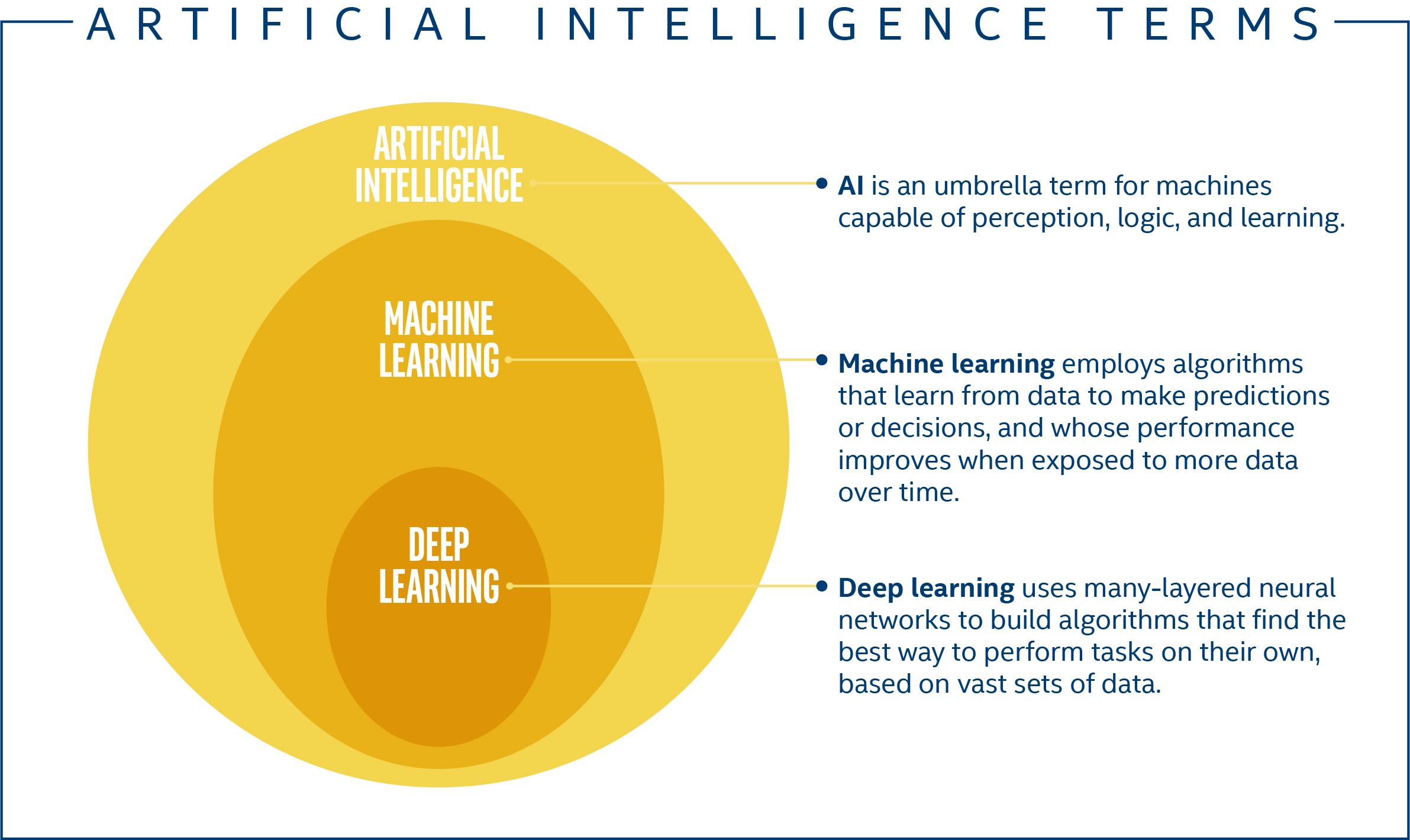
Artificial Intelligence, also known as computer science, is the study of creating intelligent machines capable to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence.
There are many kinds of artificial intelligence technology available today. These include machine learning, neural networks and expert systems, genetic algorithms and fuzzy logic. Rule-based systems, case based reasoning, knowledge representation, ontology and ontology engine technologies.
Much has been said about whether AI will ever be able to understand human thoughts. Deep learning technology has allowed for the creation of programs that can do specific tasks.
Today, Google's DeepMind unit is one of the world's largest developers of AI software. Demis Hashibis, who was previously the head neuroscience at University College London, founded the unit in 2010. DeepMind developed AlphaGo in 2014 to allow professional players to play Go.
What is the current status of the AI industry
The AI industry is growing at an unprecedented rate. By 2020, there will be more than 50 billion connected devices to the internet. This means that all of us will have access to AI technology via our smartphones, tablets, laptops, and laptops.
This shift will require businesses to be adaptable in order to remain competitive. If they don’t, they run the risk of losing customers and clients to companies who do.
Now, the question is: What business model would your use to profit from these opportunities? Do you envision a platform where users could upload their data? Then, connect it to other users. Maybe you offer voice or image recognition services?
Whatever you decide to do in life, you should think carefully about how it could affect your competitive position. Although you might not always win, if you are smart and continue to innovate, you could win big!
How does AI work
You need to be familiar with basic computing principles in order to understand the workings of AI.
Computers store data in memory. Computers work with code programs to process the information. The code tells computers what to do next.
An algorithm is a sequence of instructions that instructs the computer to do a particular task. These algorithms are usually written as code.
An algorithm can be considered a recipe. A recipe could contain ingredients and steps. Each step may be a different instruction. An example: One instruction could say "add water" and another "heat it until boiling."
What can AI be used for today?
Artificial intelligence (AI), which is also known as natural language processing, artificial agents, neural networks, expert system, etc., is an umbrella term. It is also called smart machines.
Alan Turing wrote the first computer programs in 1950. He was curious about whether computers could think. In his paper, Computing Machinery and Intelligence, he suggested a test for artificial Intelligence. The test seeks to determine if a computer programme can communicate with a human.
In 1956, John McCarthy introduced the concept of artificial intelligence and coined the phrase "artificial intelligence" in his article "Artificial Intelligence."
We have many AI-based technology options today. Some are easy to use and others more complicated. They can be voice recognition software or self-driving car.
There are two main types of AI: rule-based AI and statistical AI. Rule-based uses logic for making decisions. An example of this is a bank account balance. It would be calculated according to rules like: $10 minimum withdraw $5. Otherwise, deposit $1. Statistics are used to make decisions. For instance, a weather forecast might look at historical data to predict what will happen next.
Statistics
- The company's AI team trained an image recognition model to 85 percent accuracy using billions of public Instagram photos tagged with hashtags. (builtin.com)
- That's as many of us that have been in that AI space would say, it's about 70 or 80 percent of the work. (finra.org)
- In the first half of 2017, the company discovered and banned 300,000 terrorist-linked accounts, 95 percent of which were found by non-human, artificially intelligent machines. (builtin.com)
- A 2021 Pew Research survey revealed that 37 percent of respondents who are more concerned than excited about AI had concerns including job loss, privacy, and AI's potential to “surpass human skills.” (builtin.com)
- In 2019, AI adoption among large companies increased by 47% compared to 2018, according to the latest Artificial IntelligenceIndex report. (marsner.com)
External Links
How To
How to set Cortana up daily briefing
Cortana can be used as a digital assistant in Windows 10. It is designed to assist users in finding answers quickly, keeping them informed, and getting things done across their devices.
A daily briefing can be set up to help you make your life easier and provide useful information at all times. You can expect news, weather, stock prices, stock quotes, traffic reports, reminders, among other information. You have control over the frequency and type of information that you receive.
Win + I is the key to Cortana. Select "Cortana" and press Win + I. Select "Daily briefings" under "Settings," then scroll down until you see the option to enable or disable the daily briefing feature.
If you have the daily briefing feature enabled, here's how it can be customized:
1. Start the Cortana App.
2. Scroll down until you reach the "My Day” section.
3. Click the arrow beside "Customize My Day".
4. Choose the type of information you would like to receive each day.
5. Change the frequency of the updates.
6. Add or remove items from your shopping list.
7. You can save the changes.
8. Close the app